alignment
Where to align something along an axis.
Possible values are:
start: Aligns at the start of the text direction.end: Aligns at the end of the text direction.left: Align at the left.center: Aligns in the middle, horizontally.right: Aligns at the right.top: Aligns at the top.horizon: Aligns in the middle, vertically.bottom: Align at the bottom.
These values are available globally and also in the alignment type's scope, so you can write either of the following two:
#align(center)[Hi]
#align(alignment.center)[Hi]
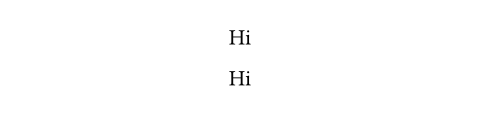
2D alignments
To align along both axes at the same time, add the two alignments using the
+ operator. For example, top + right aligns the content to the top right
corner.
#set page(height: 3cm)
#align(center + bottom)[Hi]

Fields
The x and y fields hold the alignment's horizontal and vertical
components, respectively (as yet another alignment). They may be none.
#(top + right).x \
#left.x \
#left.y (none)

定义定义这些函数和类型带有附属定义。要访问这种定义,请先写上函数或类型的名称,再加上定义的名称,并用句点在中间分隔。
定义
这些函数和类型带有附属定义。要访问这种定义,请先写上函数或类型的名称,再加上定义的名称,并用句点在中间分隔。
axis
axisThe axis this alignment belongs to.
"horizontal"forstart,left,center,right, andend"vertical"fortop,horizon, andbottomnonefor 2-dimensional alignments
展开例子
#left.axis() \
#bottom.axis()

self.axis()inv
invThe inverse alignment.
展开例子
#top.inv() \
#left.inv() \
#center.inv() \
#(left + bottom).inv()

self.inv()->