Calculation
Module for calculations and processing of numeric values.
These definitions are part of the calc module and not imported by default.
In addition to the functions listed below, the calc module also defines
the constants pi, tau, e, inf, and nan.
Function
abs
absCalculates the absolute value of a numeric value.
#calc.abs(-5) \
#calc.abs(5pt - 2cm) \
#calc.abs(2fr)

calc.abs()->anypow
powRaises a value to some exponent.
#calc.pow(2, 3)

calc.pow(,)->exp
expRaises a value to some exponent of e.
#calc.exp(1)

calc.exp()->sqrt
sqrtCalculates the square root of a number.
#calc.sqrt(16) \
#calc.sqrt(2.5)
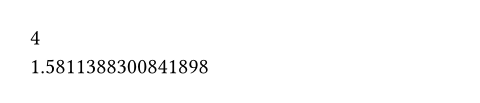
calc.sqrt()->root
rootCalculates the real nth root of a number.
If the number is negative, then n must be odd.
#calc.root(16.0, 4) \
#calc.root(27.0, 3)

calc.root(,)->sin
sinCalculates the sine of an angle.
When called with an integer or a float, they will be interpreted as radians.
#assert(calc.sin(90deg) == calc.sin(-270deg))
#calc.sin(1.5) \
#calc.sin(90deg)

calc.sin()->cos
cosCalculates the cosine of an angle.
When called with an integer or a float, they will be interpreted as radians.
#calc.cos(90deg) \
#calc.cos(1.5) \
#calc.cos(90deg)

calc.cos()->tan
tanCalculates the tangent of an angle.
When called with an integer or a float, they will be interpreted as radians.
#calc.tan(1.5) \
#calc.tan(90deg)

calc.tan()->asin
asinCalculates the arcsine of a number.
#calc.asin(0) \
#calc.asin(1)

calc.asin()->acos
acosCalculates the arccosine of a number.
#calc.acos(0) \
#calc.acos(1)

calc.acos()->atan
atanCalculates the arctangent of a number.
#calc.atan(0) \
#calc.atan(1)

calc.atan()->atan2
atan2Calculates the four-quadrant arctangent of a coordinate.
The arguments are (x, y), not (y, x).
#calc.atan2(1, 1) \
#calc.atan2(-2, -3)

calc.atan2(,)->sinh
sinhCalculates the hyperbolic sine of a hyperbolic angle.
#calc.sinh(0) \
#calc.sinh(1.5)

calc.sinh()->value
valueThe hyperbolic angle whose hyperbolic sine to calculate.
cosh
coshCalculates the hyperbolic cosine of a hyperbolic angle.
#calc.cosh(0) \
#calc.cosh(1.5)

calc.cosh()->value
valueThe hyperbolic angle whose hyperbolic cosine to calculate.
tanh
tanhCalculates the hyperbolic tangent of an hyperbolic angle.
#calc.tanh(0) \
#calc.tanh(1.5)

calc.tanh()->value
valueThe hyperbolic angle whose hyperbolic tangent to calculate.
log
logCalculates the logarithm of a number.
If the base is not specified, the logarithm is calculated in base 10.
#calc.log(100)

calc.log(,base:)->ln
lnCalculates the natural logarithm of a number.
#calc.ln(calc.e)

calc.ln()->fact
factCalculates the factorial of a number.
#calc.fact(5)

calc.fact()->number
numberThe number whose factorial to calculate. Must be non-negative.
perm
permCalculates a permutation.
Returns the k-permutation of n, or the number of ways to choose k
items from a set of n with regard to order.
$ "perm"(n, k) &= n!/((n - k)!) \
"perm"(5, 3) &= #calc.perm(5, 3) $
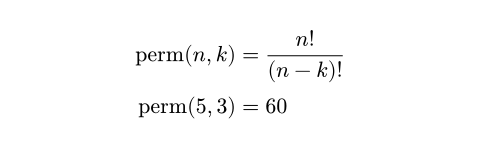
calc.perm(,)->binom
binomCalculates a binomial coefficient.
Returns the k-combination of n, or the number of ways to choose k
items from a set of n without regard to order.
#calc.binom(10, 5)

calc.binom(,)->gcd
gcdCalculates the greatest common divisor of two integers.
#calc.gcd(7, 42)

calc.gcd(,)->lcm
lcmCalculates the least common multiple of two integers.
#calc.lcm(96, 13)

calc.lcm(,)->floor
floorRounds a number down to the nearest integer.
If the number is already an integer, it is returned unchanged.
#assert(calc.floor(3.14) == 3)
#assert(calc.floor(3) == 3)
#calc.floor(500.1)

calc.floor()->ceil
ceilRounds a number up to the nearest integer.
If the number is already an integer, it is returned unchanged.
#assert(calc.ceil(3.14) == 4)
#assert(calc.ceil(3) == 3)
#calc.ceil(500.1)

calc.ceil()->trunc
truncReturns the integer part of a number.
If the number is already an integer, it is returned unchanged.
#assert(calc.trunc(3) == 3)
#assert(calc.trunc(-3.7) == -3)
#calc.trunc(15.9)

calc.trunc()->fract
fractReturns the fractional part of a number.
If the number is an integer, returns 0.
#assert(calc.fract(3) == 0)
#calc.fract(-3.1)
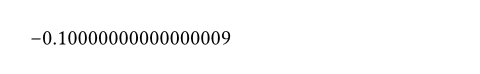
calc.fract()->round
roundRounds a number to the nearest integer.
Optionally, a number of decimal places can be specified.
#assert(calc.round(3.14) == 3)
#assert(calc.round(3.5) == 4)
#calc.round(3.1415, digits: 2)

calc.round(,)->clamp
clampClamps a number between a minimum and maximum value.
#assert(calc.clamp(5, 0, 10) == 5)
#assert(calc.clamp(5, 6, 10) == 6)
#calc.clamp(5, 0, 4)

calc.clamp(,,)->min
minDetermines the minimum of a sequence of values.
#calc.min(1, -3, -5, 20, 3, 6) \
#calc.min("typst", "in", "beta")

calc.min(any)->anyvaluesany必需参数必需参数必需参数在调用函数时必须传入。位置参数位置参数位置参数按顺序传入,不带参数名。变长参数变长参数变长参数可以传入多次。
valuesThe sequence of values from which to extract the minimum. Must not be empty.
max
maxDetermines the maximum of a sequence of values.
#calc.max(1, -3, -5, 20, 3, 6) \
#calc.max("typst", "in", "beta")

calc.max(any)->anyvaluesany必需参数必需参数必需参数在调用函数时必须传入。位置参数位置参数位置参数按顺序传入,不带参数名。变长参数变长参数变长参数可以传入多次。
valuesThe sequence of values from which to extract the maximum. Must not be empty.
even
evenDetermines whether an integer is even.
#calc.even(4) \
#calc.even(5) \
#range(10).filter(calc.even)

calc.even()->value
valueThe number to check for evenness.
odd
oddDetermines whether an integer is odd.
#calc.odd(4) \
#calc.odd(5) \
#range(10).filter(calc.odd)
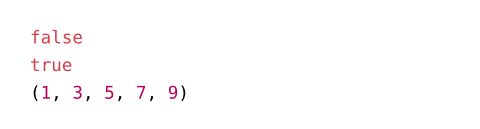
calc.odd()->value
valueThe number to check for oddness.
rem
remCalculates the remainder of two numbers.
The value calc.rem(x, y) always has the same sign as x, and is smaller
in magnitude than y.
#calc.rem(7, 3) \
#calc.rem(7, -3) \
#calc.rem(-7, 3) \
#calc.rem(-7, -3) \
#calc.rem(1.75, 0.5)

calc.rem(,)->div-euclid
div-euclidPerforms euclidean division of two numbers.
The result of this computation is that of a division rounded to the integer
n such that the dividend is greater than or equal to n times the divisor.
#calc.div-euclid(7, 3) \
#calc.div-euclid(7, -3) \
#calc.div-euclid(-7, 3) \
#calc.div-euclid(-7, -3) \
#calc.div-euclid(1.75, 0.5)

calc.div-euclid(,)->rem-euclid
rem-euclidThis calculates the least nonnegative remainder of a division.
Warning: Due to a floating point round-off error, the remainder may equal the absolute value of the divisor if the dividend is much smaller in magnitude than the divisor and the dividend is negative. This only applies for floating point inputs.
#calc.rem-euclid(7, 3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(7, -3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(-7, 3) \
#calc.rem-euclid(-7, -3) \
#calc.rem(1.75, 0.5)

calc.rem-euclid(,)->quo
quoCalculates the quotient (floored division) of two numbers.
$ "quo"(a, b) &= floor(a/b) \
"quo"(14, 5) &= #calc.quo(14, 5) \
"quo"(3.46, 0.5) &= #calc.quo(3.46, 0.5) $
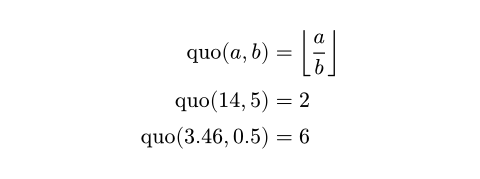
calc.quo(,)->