state
Manages stateful parts of your document.
Let's say you have some computations in your document and want to remember the result of your last computation to use it in the next one. You might try something similar to the code below and expect it to output 10, 13, 26, and 21. However this does not work in Typst. If you test this code, you will see that Typst complains with the following error message: Variables from outside the function are read-only and cannot be modified.
#let x = 0
#let compute(expr) = {
x = eval(
expr.replace("x", str(x))
)
[New value is #x. ]
}
#compute("10") \
#compute("x + 3") \
#compute("x * 2") \
#compute("x - 5")
State and document markup
Why does it do that? Because, in general, this kind of computation with side effects is problematic in document markup and Typst is upfront about that. For the results to make sense, the computation must proceed in the same order in which the results will be laid out in the document. In our simple example, that's the case, but in general it might not be.
Let's look at a slightly different, but similar kind of state: The heading numbering. We want to increase the heading counter at each heading. Easy enough, right? Just add one. Well, it's not that simple. Consider the following example:
#set heading(numbering: "1.")
#let template(body) = [
= Outline
...
#body
]
#show: template
= Introduction
...

Here, Typst first processes the body of the document after the show rule,
sees the Introduction heading, then passes the resulting content to the
template function and only then sees the Outline. Just counting up would
number the Introduction with 1 and the Outline with 2.
Managing state in Typst
So what do we do instead? We use Typst's state management system. Calling
the state function with an identifying string key and an optional initial
value gives you a state value which exposes a few methods. The two most
important ones are display and update:
-
The
displaymethod shows the current value of the state. You can optionally give it a function that receives the value and formats it in some way. -
The
updatemethod modifies the state. You can give it any value. If given a non-function value, it sets the state to that value. If given a function, that function receives the previous state and has to return the new state.
Our initial example would now look like this:
#let s = state("x", 0)
#let compute(expr) = [
#s.update(x =>
eval(expr.replace("x", str(x)))
)
New value is #s.display().
]
#compute("10") \
#compute("x + 3") \
#compute("x * 2") \
#compute("x - 5")

State managed by Typst is always updated in layout order, not in evaluation
order. The update method returns content and its effect occurs at the
position where the returned content is inserted into the document.
As a result, we can now also store some of the computations in variables, but they still show the correct results:
...
#let more = [
#compute("x * 2") \
#compute("x - 5")
]
#compute("10") \
#compute("x + 3") \
#more

This example is of course a bit silly, but in practice this is often exactly what you want! A good example are heading counters, which is why Typst's counting system is very similar to its state system.
Time Travel
By using Typst's state management system you also get time travel
capabilities! By combining the state system with locate and
query, we can find out what the value of the state will be at
any position in the document from anywhere else. In particular, the at
method gives us the value of the state at any location and the final
methods gives us the value of the state at the end of the document.
...
Value at `<here>` is
#locate(loc => s.at(
query(<here>, loc)
.first()
.location()
))
#compute("10") \
#compute("x + 3") \
*Here.* <here> \
#compute("x * 2") \
#compute("x - 5")
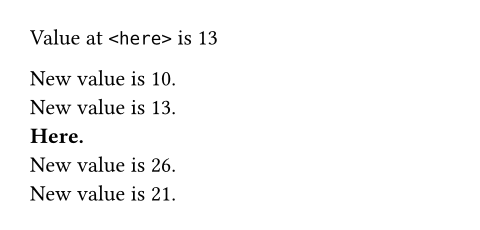
A word of caution
To resolve the values of all states, Typst evaluates parts of your code multiple times. However, there is no guarantee that your state manipulation can actually be completely resolved.
For instance, if you generate state updates depending on the final value of
a state, the results might never converge. The example below illustrates
this. We initialize our state with 1 and then update it to its own final
value plus 1. So it should be 2, but then its final value is 2, so it
should be 3, and so on. This example display 4 because Typst simply
gives up after a few attempts.
#let s = state("x", 1)
#locate(loc => {
s.update(s.final(loc) + 1)
})
#s.display()

In general, you should typically not generate state updates from within
locate calls or display calls of state or counters. Instead, pass a
function to update that determines the value of the state based on its
previous value.
构造函数参数参数是传给函数的输入,写在函数名后的括号中。
Create a new state identified by a key.
state(,any)->key
keyThe key that identifies this state.
initany位置参数位置参数位置参数按顺序传入,不带参数名。
initThe initial value of the state.
默认值:none
定义定义这些函数和类型带有附属定义。要访问这种定义,请先写上函数或类型的名称,再加上定义的名称,并用句点在中间分隔。
display
displayDisplays the current value of the state.
self.display()->update
updateUpdate the value of the state.
The update will be in effect at the position where the returned content
is inserted into the document. If you don't put the output into the
document, nothing happens! This would be the case, for example, if you
write let _ = state("key").update(7). State updates are always
applied in layout order and in that case, Typst wouldn't know when to
update the state.
self.update()->update
updateIf given a non function-value, sets the state to that value. If given a function, that function receives the previous state and has to return the new state.
at
atGet the value of the state at the given location.
self.at()->anyfinal
finalGet the value of the state at the end of the document.
self.final()->anylocation
locationCan be an arbitrary location, as its value is irrelevant for the
method's return value. Why is it required then? As noted before,
Typst has to evaluate parts of your code multiple times to determine
the values of all state. By only allowing this method within
locate calls, the amount of code that can depend on the
method's result is reduced. If you could call final directly at
the top level of a module, the evaluation of the whole module and
its exports could depend on the state's value.